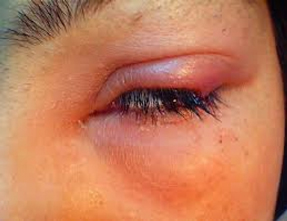
 A stye is a small, painful lump on the inside or outside of the eyelid. If you have a stye, your eye may also be watery and you may have a red eye or eyelid.
A stye is a small, painful lump on the inside or outside of the eyelid. If you have a stye, your eye may also be watery and you may have a red eye or eyelid.
A stye – also clled a hordeolum – usually only affects one eye, although it’s possible to have styes in both eyes or to have more than one stye in the same eye. Your vision shouldn’t be affected. Types of stye
There are two types of stye. They are: external stye (external hordeolum) – a swelling that develops along the edge of your eyelid; it may turn into a yellow pus-filled spot that is painful to touch internal stye (internal hordeolum) – a swelling that develops on the inside of your eyelid; it’s usually more painful than an external stye
What causes a stye? Styes are usually caused by an infection with staphylococcus bacteria (staphylococcal infection). Long-term blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids) may also increase the risk of developing a stye. Styes are fairly common and you may have at least one or two during your lifetime.
Frequently, bacteria can enter and infect an eyelid oil gland, which are present in both the upper and lower eyelids, causing increased inflammation, pain, and redness of the eye, and even redness of the surrounding eyelid and cheek tissue. The medical term for stye is hordeolum.
