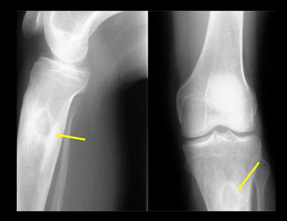
 Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone, a rare but serious condition. Bones can become infected in a number of ways: Infection in one part of the body may spread through the bloodstream into the bone, or an open fracture or surgery may expose the bone to infection
Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone, a rare but serious condition. Bones can become infected in a number of ways: Infection in one part of the body may spread through the bloodstream into the bone, or an open fracture or surgery may expose the bone to infection
What Causes Osteomyelitis?
In most cases, a bacteria called Staphylococcus aureus, a type of staphbacteria, causes osteomyelitis.
Certain chronic conditions like diabetes may increase your risk for osteomyelitis.
Who Gets Osteomyelitis?
Only 2 out of every 10,000 people get osteomyelitis. The condition affects children and adults, although in different ways. Certain conditions and behaviors that weaken the immune system increase a person’s risk for osteomyelitis, including:
- Diabetes (most cases of osteomyelitis stem from diabetes)
- Sickle cell disease
- HIV or AIDS
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Intravenous drug use
- Alcoholism
- Long-term use of steroids
- Hemodialysis
- Poor blood supply
- Recent injury
Bone surgery, including hip and knee replacements, also increase the chance of bone infection.
