 Filariasis (or philariasis) is a parasitic disease caused by an infection with roundworms of the Filarioidea type. These are spread by blood-feeding black flies and mosquitoes. This disease belongs to the group of diseases called helminthiasis. Eight known filarial nematodes use humans as their definitive hosts
Filariasis (or philariasis) is a parasitic disease caused by an infection with roundworms of the Filarioidea type. These are spread by blood-feeding black flies and mosquitoes. This disease belongs to the group of diseases called helminthiasis. Eight known filarial nematodes use humans as their definitive hosts
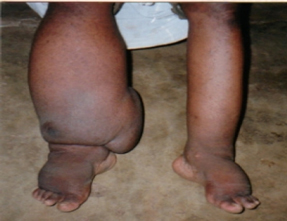
Lymphatic filariasis, commonly known as elephantiasis, is a neglected tropical disease. Infection occurs when filarial parasites are transmitted to humans through mosquitoes. Infection is usually acquired in childhood causing hidden damage to the lymphatic system.
The painful and profoundly disfiguring visible manifestations of the disease, lymphoedema, elephantiasis and scrotal swelling occur later in life and lead to permanent disability. These patients are not only physically disabled, but suffer mental, social and financial losses contributing to stigma and poverty.
Lymphatic filariasis is infection with the filarial worms, Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi or B. timori. These parasites are transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito and develop into adult worms in the lymphatic vessels, causing severe damage and swelling (lymphoedema). Elephantiasis – painful, disfiguring swelling of the legs and genital organs – is a classic sign of late-stage disease.
