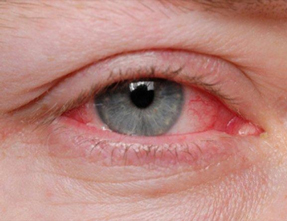
 Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye is inflammation of the conjunctiva (the outermost layer of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids). It is commonly due to an infection (usually viral, but sometimes bacterial or parasitic), or an allergic reaction.
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye is inflammation of the conjunctiva (the outermost layer of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids). It is commonly due to an infection (usually viral, but sometimes bacterial or parasitic), or an allergic reaction.
Conjunctivitis can affect one or both eyes and is the most likely diagnosis in someone with eye redness and discharge (fluid coming from the eye). The affected eye is often “stuck shut” in the morning. Bacterial and viral conjunctivitis are highly contagious, and are transmitted through contact with the discharge. Generally speaking, conjunctivitis will go away on its own and poses no serious health risk. Eye drops can help relieve symptoms and, for bacterial causes, likely reduce the length of the illness if given early.
Conjunctivitis is a common condition that causes redness and inflammation of the thin layer of tissue that covers the front of the eye (the conjunctiva).
Other symptoms of conjunctivitis include itchiness and watering of the eyes, and sometimes a sticky coating on the eyelashes (if it’s caused by an allergy). Read more about the symptoms of conjunctivitis.
Conjunctivitis can affect one eye at first, but usually affects both eyes after a few hours.
