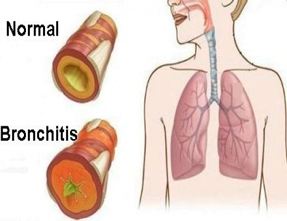
 Your bronchial tubes are responsible for delivering air to your lungs. When these tubes become inflamed, mucus can build up. The coughing and shortness of breath this causes is known as bronchitis. People often develop acute bronchitis after a viral chest infection.
Your bronchial tubes are responsible for delivering air to your lungs. When these tubes become inflamed, mucus can build up. The coughing and shortness of breath this causes is known as bronchitis. People often develop acute bronchitis after a viral chest infection.
It is important to distinguish acute bronchitis from chronic bronchitis. Acute bronchitis usually lasts less than 10 days. However the coughing can continue for several weeks after the inflammation has cleared. Chronic bronchitis can last for several weeks and usually comes back.
The most common cause of acute bronchitis is a viral upper respiratory infection. Both the common cold and influenza can lead to acute bronchitis. In rare cases, the bacterium that causes whooping cough can also cause acute bronchitis. This bacterium is called Bordetella pertussis.
The symptoms of acute bronchitis are not specific. They mimic symptoms of other conditions such as chronic cough, chronic bronchitis, postnasal drip, and pneumonia. Therefore, acute diagnosis must always be diagnosed by a doctor.
Common symptoms of acute bronchitis include:
- chronic cough, which may continue beyond 10 days and contain clear or colored mucus
- shortness of breath
- wheezing
- low-grade fever (a high fever may be an indication of a secondary infection such as pneumonia)
- chest pain
- chest tightness
- sore throat from persistent coughing
