 Gynecomastia is swelling of the breast tissue in boys or men, caused by an imbalance of the hormones estrogen and testosterone. Gynecomastia can affect one or both breasts, sometimes unevenly. Newborns, boys going through puberty and older men may develop gynecomastia as a result of normal changes in hormone levels, though other causes also exist.
Gynecomastia is swelling of the breast tissue in boys or men, caused by an imbalance of the hormones estrogen and testosterone. Gynecomastia can affect one or both breasts, sometimes unevenly. Newborns, boys going through puberty and older men may develop gynecomastia as a result of normal changes in hormone levels, though other causes also exist.
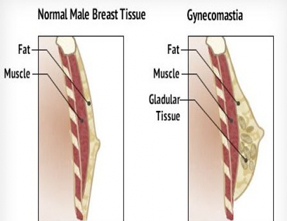
Gynecomastia is enlargement of the gland tissue of the male breast. During infancy, puberty, and in middle-aged to older men, gynecomastia can be common. Gynecomastia must be distinguished from pseudogynecomastia or lipomastia, which refers to the presence of fat deposits in the breast area of obese men. True gynecomastia results from growth of the glandular, or breast tissue, which is present in very small amounts in men. Gynecomastia is the most common reason for medical evaluation of the male breast.
Gynecomastia results from an imbalance in hormone levels in which levels of estrogen (female hormones) are increased relative to levels of androgens (male hormones). Gynecomastia that occurs in normally-growing infant and pubertal boys that resolves on its own with time is known as physiologic gynecomastia.
