 Most cases of gallstones don’t cause any symptoms. But if a gallstone blocks one of the bile ducts, it can cause sudden, severe abdominal pain, known as biliary colic. Other symptoms may develop if the blockage is more severe or develops in another part of the digestive system.
Most cases of gallstones don’t cause any symptoms. But if a gallstone blocks one of the bile ducts, it can cause sudden, severe abdominal pain, known as biliary colic. Other symptoms may develop if the blockage is more severe or develops in another part of the digestive system.
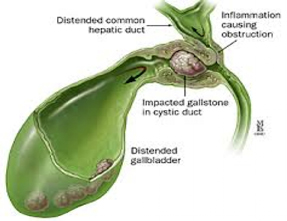
Gallstones are the most common reason for biliary colic. If a gallstone blocks either of these ducts, the normal flow of bile into the intestine is disrupted. The muscle cells in the bile duct contract vigorously to try to move the stone, causing the pain of biliary colic. A stricture of the bile duct or a tumor also can block bile flow and cause biliary colic.
