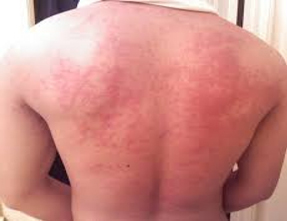
 A food allergy is caused when your immune system mistakenly treats harmless proteins found in certain foods as a threat. It releases a number of chemicals, which then triggers an allergic reaction. The immune system protects the body by producing specialised proteins called antibodies.
A food allergy is caused when your immune system mistakenly treats harmless proteins found in certain foods as a threat. It releases a number of chemicals, which then triggers an allergic reaction. The immune system protects the body by producing specialised proteins called antibodies.
Antibodies identify potential threats to your body, such as bacteria and viruses. They then signal to your immune system to release chemicals to kill the threat and prevent the spread of infection. In the most common type of food allergy, an antibody known as immunoglobulin E (IgE) mistakenly targets a certain protein found in food as a threat. IgE can cause several chemicals to be released, the most important
