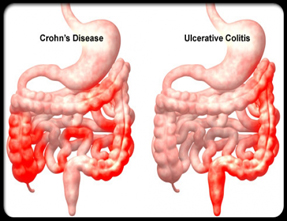
 Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). As the name implies, inflammatory bowel diseases cause inflammation of the intestinal tract. The intestinal tract includes your mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), rectum, and anus.
Crohn’s disease is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). As the name implies, inflammatory bowel diseases cause inflammation of the intestinal tract. The intestinal tract includes your mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), rectum, and anus.
The inflammation and irritation of Crohn’s disease can occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract but is most common in the lower portion of the small intestine (the ileum). It is sometimes calledregional enteritis because diseased areas are often interspersed with healthy areas—in other words, they only affect some regions of the GI tract.
