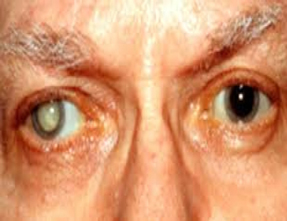
 A cataract is a clouding of the lens in the eye leading to a decrease in vision. It can affect one or both eyes. Often it develops slowly. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and trouble seeing at night.This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing
A cataract is a clouding of the lens in the eye leading to a decrease in vision. It can affect one or both eyes. Often it develops slowly. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry vision, halos around light, trouble with bright lights, and trouble seeing at night.This may result in trouble driving, reading, or recognizing
faces. Poor vision may also result in an increased risk of falling anddepression. Cataracts are the cause of half of blindness and 33% of visual impairment worldwide.
Cataracts are most commonly due to aging, but may also occur due to trauma, radiation exposure, be present from birth, or occur following eye surgery for other problems. Risk factors include diabetes, smoking tobacco, prolonged exposure to sunlight, and alcohol. Either clumps of protein or yellow-brown pigment may be deposited in the lens reducing the transmission of light to theretina at the back of the eye. Diagnosis is by an eye examination.
Prevention includes wearing sunglasses and not smoking. Early on the symptoms may be improved with eyeglasses. If this does not help, surgery to remove the cloudy lens and replace it with an artificial lens is the only effective treatment. Surgery is only needed if the cataracts are causing problems. Surgery generally results in an improved quality of life.Cataract surgery is not easily available in many countries, which is especially true for women.
About 20 million people globally are blind due to cataracts. It is the cause of about 5% of blindness in the United States and nearly 60% of blindness in parts of Africa and South America. Blindness from cataracts occurs in about 10 to 40 per 100,000 children in the developing world and 1 to 4 per 100,000 children in the developed world. Cataracts become more common with age. About half the people in the United States have had cataracts by the age of 80.
