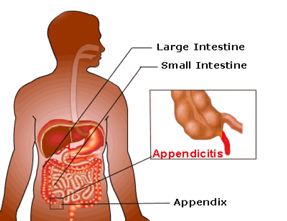
 Appendicitis refers to inappropriate activity of the vermiform appendix, a worm-shaped extension of the colon. Appendicitis is a very serious illness and can be life-threatening if it is not treated in time. Appendicitis affects about 6 – 7 percent of the population in the United States and Europe.
Appendicitis refers to inappropriate activity of the vermiform appendix, a worm-shaped extension of the colon. Appendicitis is a very serious illness and can be life-threatening if it is not treated in time. Appendicitis affects about 6 – 7 percent of the population in the United States and Europe.
What is Appendicitis?
Appendicitis refers to inappropriate activity of the vermiform appendix, a worm-shaped extension of the colon.
There are 2 basic types of Appendicitis, acute and chronic.
Symptoms of appendicitis are intense and painful, continuous abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation or diarrhea and fever.
The pain usually begins in the lower region of the abdomen and later shifts to the lower right side. Generally the pain will intensify with physical effort.
Anyone can develop appendicitis, regardless of age and sex but the illness has a higher incidence in males. Children between 3 – 15 for some reason are also at risk of developing acute appendicitis. Elderly people and patients with medical problems usually develop atypical acute appendicitis.
Appendicitis is a serious illness and can be life-threatening if it is not treated in time. Appendicitis affects about 6 – 7 percent of the population in the United States and Europe. People with symptoms of appendicitis should not take laxatives or enemas to relieve constipation because these medicines could cause the appendix to burst.
What is Acute Appendicitis?
Acute appendicitis is considered to be the most common cause of abdominal pain and distress in children and teenagers worldwide. Acute appendicitis develops very fast and is much simpler to detect, in most cases it requires immediate surgery.
Acute appendicitis refers to complete obstruction of the vermiform appendix. Bacterial infections are also a cause of acute appendicitis. The appendix is a tubular extension of the large intestine and its function is thought to be related with the process of digestion. When the appendix is blocked by calculus and faeces or it is squeezed by the lymph nodes (due to bacterial infection, the lymph nodes usually become swollen and press against the appendix), it swells and usually doesn’t receive enough blood. Bacteria grow inside the appendix, eventually causing its death. In acute appendicitis, the inflammation of the appendix is serious and can lead to complications (perforation, gangrene, sepsis). Acute appendicitis is a surgical emergency and most patients with this form of illness already have complications before entering the operation room
